Did you know that a migrant worker from Sub-Saharan Africa pays the highest fees globally to send money home? According to the World Bank, transferring $200 to the area costs 8.5%. However, the problem is not limited to this part of the world: remittances ― sums of money sent in payment ― on an average cost 7% when transferred globally. As such payments are a critical source of funding for developing countries, the UN set a target to cut these costs to 3% over the next decade.
Get In Touch
Lowering the frictions of cross-border payments, particularly to those who need them most, is a noble goal. The problem is, cross-border payments have always involved a chain of intermediaries. When traditional banking costs too much to be inclusive, parties on both sides of a transaction are burdened with the inconvenience, risk, fees, and high costs of negotiating the handoffs and currency exchanges to get a transaction safely from sender to recipient. There are other barriers: according to an OECD paper, a key cost driver of international payments is compliance with rules for KYC. Despite the emergence of digital challengers, fees remain relatively high.
Blockchain holds the potential to greatly reduce the number of intermediaries required in cross-border transactions, making remittances cheaper and faster to execute.
Many hope cryptocurrencies can be used as a bridge asset. For example, instead of making pricey foreign exchange transactions between US dollars and South Sudanese pounds, a cryptocurrency could be directly transferred to the recipient who then can exchange it locally. By using smart contracts, blockchain could help reduce bureaucratic overhead and partially automate regulatory compliance.
Blockchain Barriers
Blockchain has fallen short of its potential for the following reasons:
-
Impractical
The average user struggles to manage wallets and private keys on their own, whereas centralized exchanges charge additional fees. -
Volatile
The extreme volatility of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin make them unviable for everyday transactions.
-
-
Rigid
Most existing blockchain solutions cannot handle the transaction throughput required to operate a payment network. -
Insecure
Existing blockchains using Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Authority (PoA), or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms offer between 33% and 50% Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), which could be potentially breached by a well-financed and coordinated cyberattack, particularly by a state actor.
The Geeq Difference
Radically increasing speed while reducing transaction costs for payments and remittances down to fractions of a cent.
Get In Touch-
Inexpensive
Geeq offers low transaction fees, even for very small, frequent payments. -
Stable
Geeq places strong emphasis on reducing uncertainty and minimizing volatility in transaction fees. -
Scalable
Geeq’s Proof-of-Honesty consensus mechanism does not rely on mining, enabling high transactional throughput with less latency, while consuming far fewer resources than traditional blockchain solutions. -
Secure
Financial transactions require bullet-proof security. The degree of security provided by Geeq – using mechanisms like the Good Behavior Bond and Proof-of-Honesty – is unrivaled. -
Flexible
Different countries and their people have access to varying degrees of connectivity. Geeq’s unique technology provides a range of solutions to work for those with intermittent access.
YOU HAVE QUESTIONS
We have answers…
Geeq Payments – Remittances
After two decades of growth that saw remittance flows to low and middle-income countries (LMICs) reach a record high of $548 billion in 2019, the World Bank now forecasts significant declines.
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, remittances to LMICs are projected to fall to $470 billion by 2021, a 14% drop over two years. For comparison, remittances fell 5% due to the global financial crisis in 2009.
Migrant workers make an essential contribution to their countries of origin. In 2019, remittance flows to LMICs equated to three times all official development assistance combined and exceeded foreign direct investment (FDI).
Unfortunately, remittances incur high transaction fees, with some of the poorest regions hardest hit. A migrant worker sending money to sub-Saharan Africa, for example, pays an average transaction fee of 8.5% to send $200. In terms of poverty alleviation, such fees are concerning. Also, when transaction costs are higher, frequency of remittances decline.
The United Nations takes the problem very seriously: by 2030, the international community aims to reduce average global remittance costs to 3%. However, data shows reaching this global target on time might be a difficult task. Despite modest improvements mainly due to technological advancements, global remittance fees remain high.
Disruption through Digitization
There is a common perception that mobile phones, combined with the demographics of a far younger and larger percentage of young people in Sub-Saharan African countries compared to the rest of the world, may give those countries a boost to adopt digital currencies.
Let’s dig deeper into the details. A Pew Research Study in 2018 confirms tremendously high ownership of mobile phones in these countries, between 75-91%. However, of those who own phones, the majority have basic phones, such as a flip phone compared to smart phones. The result? The largest innovator in the fintech space has been M-Pesa, a mobile banking service. M-Pesa, working with telecommunications company Safaricom, has made it easy to transfer cash via text message. As of 2019, M-Pesa had more than 30 million users in Kenya and more than 31.4 million users outside Kenya.
What are some of the ingredients for M-Pesa’s success?
- Easy to understand instructions.
- A reduced need to carry cash, while still being able to transact in cash.
- The ability to make payments at retail outlets.
- The ability to transfer cash to others, whether they are in the same telecom network or not.
Are consumers in other Sub-Saharan African countries ready to follow suit? It depends. According to The African Leapfrog Index, South Africa is the second highest user of mobile money payments, with 60% of the population having made digital payments in 2017 compared to Kenya’s 70%.
There are many prerequisites for technology adoption, however, and other countries are not at the same stage. For example, the same studies showed only 5.8% of those in Egypt made a digital payment in 2017 and 80% of those in Nigeria (known for its embrace of innovation otherwise) had never heard of mobile money.
What about the predicted use for digital currencies? Even if digital payment applications were the norm, the price volatility of most cryptocurrencies suggest they would not be suitable for remittances.
Digitization without Disintermediation
The M-Pesa model teaches us some of the conditions to replicate to encourage adoption of new payment technologies. It also serves to remind us that digitization is not the same as disintermediation. M-Pesa is successful because it disrupted banking with digitization. It still enjoys all the powers of being an intermediary.
Fees: M-Pesa charges a fee to withdraw cash and another fee to transfer cash. Fees depend on whether the recipient is in network or not, and vary depending on the amount sent. Fees are high and regressive: the lower the cash transfer, the higher the percentage charged as a fee. (On May 12, 2021, only the first $0.46 may be withdrawn from a M-Pesa agent for free, and charges for sending payments begin at $0.93.)
Limits: M-Pesa has the power to cap daily transactions. For example, small or medium sized businesses were limited to $700 per day before Covid19. (During 2020, M-Pesa waived some fees and raised the daily limit.)
Identification: In order to register for a M-Pesa account in Kenya, customers must show a valid government ID such as the Kenyan national identification card or a passport.
Lessons for Remittances: Decentralized Blockchain Payments
As we’ve argued elsewhere, intermediaries in financial markets incur fees which they pass onto their customers. While these costs may be easily absorbed by the rich, they are prohibitively high for the economically vulnerable. While mobile banking applications have led to dramatic increases in economic activity for many, what happens if your most valuable transactions are small? What happens when wages fall due to economic shocks like Covid, and the money you have available for remittances shrinks?
We have observed part of the recipe for success. Provide what consumers want: ease of use, reduced needs to carry and track cash, and the ability to interact with anyone. Be realistic about existing infrastructure and regulatory constraints. Eliminate limits on transactions by removing the power of an intermediary to impose requirements. Finally, provide a payments platform that lowers costs so much it is able to compete with, or be adopted by, existing financial services providers. It has never been possible to bring all these ingredients together – until now.
Why Hasn’t Blockchain Solved These Problems Already?
Blockchain platforms were never designed to cope with the volume of small payments that ordinary people make while going about our daily lives. Private blockchains fail to provide a sensible alternative to cash: they are expensive to implement, limited in scope, clunky by design, and as potentially corruptible as whoever puts them in place. Public blockchains have failed as well, by focusing on disruption in finance rather than payments.
In fact, many blockchain platforms have structured their technologies in ways that make small transactions more difficult than the status quo. When security models depend on participants who are willing to burn resources, they give up the opportunity to lower costs through decentralization. When people must lock up capital or try to understand complex rules in order to participate, incentives are created for agglomeration, delegation, and concentration – leading right back to the organizational forms that have solved these problems for all time, albeit with different financiers. Blockchains such as these do not serve people who simply want timely, uncomplicated, and inexpensive payment solutions.
Geeq Payments : A Thoroughly Practical Approach
Geeq is a public blockchain platform, with architecture that scales to handle any volume of transactions. Described at the most basic level, distributed ledger technologies provide a way to keep track of digital transactions. By focusing on the cost-savings from putting decentralized technology to work, Geeq’s payment platform lowers the cost of a basic transaction to less than one 1/100th of a cent using a typical US household’s broadband. Geeq is reinventing blockchain to make it technologically and economically feasible to send any number of transactions, of any size, including remittances.
As mentioned earlier, countries differ in the state of their infrastructure. The African Leapfrog Index indicates plenty of room to grow in mobile payments, as well as crucial awareness and support from governments that aim to cross the digital divide. Nonetheless, the reality on the ground includes frequent power outages as well as less take-up in older age brackets and more rural communities. To provide utility in these cases, true adoption of Geeq payments requires more targeted approaches.
Geeq’s patent-pending token categories may be used when access to connectivity is difficult and intermittent. Geeq’s certified bearer tokens do not even require the recipient to be the one to redeem them. Geeq has the potential to be the key enabling technology for regular, stable remittances, as well as support all the small payments that make up daily life.
In Kenya, at current prices, M-Pesa charges 5% or $0.23 in Kenya to send $4.67. Geeq’s patent-pending token technologies do not require an intermediary to coordinate liquidity or set fee schedules, because Geeq transactions, applications, and blockchain validation are all decentralized. Such innovation is essential to meet the UN’s ambitious 3% target. Most importantly, these payment technologies will be able to provide more financial security and a better quality of life for all who rely on them.
Geeq is a multi-blockchain platform secured by our Proof of Honesty protocol (PoH), safe enough for your most valuable data, cheap enough for IoT, and flexible enough for any use.
close
The World Bank — Using Blockchain to Further its Mission
This article is an excerpt of work commissioned by the Chief Economist’s Office of Equitable Growth, Finance, and Institutions Practice as part of the World Bank Productivity Project. All opinions expressed in this article are our own and do not represent the official stance of The World Bank.
The stated mission of the World Bank is to end extreme poverty by reducing the share of the global population that lives in extreme poverty to 3 percent by 2030 and to promote shared prosperity by increasing the incomes of the poorest 40 percent of people in every country. A key driver for this is increasing financial and social inclusion, especially of poor and marginalized populations.
One of the primary application spaces for blockchain is Fintech. Bitcoin was launched in 2009 as an experimental payment mechanism that was self-supporting and completely independent of any government or institution. Ethereum was launched in 2013 and built on this idea by adding smart contracts that allowed agents to make binding commitments without a Trusted Data Intermediary (TDI). The third largest cryptocurrency powers the Ripple network which is an interbank settlement system meant to compete with SWIFT. Most of the other top twenty blockchain platforms support “alt-coins” which compete with Bitcoin and Ethereum. Many other startups exist to provide brokerage, payments, international transfers, custody solutions for securities, derivatives of various kinds, loans, and a wide array of other financial services. There are even a number of blockchain startups whose purpose is to help other blockchain startups get funding.
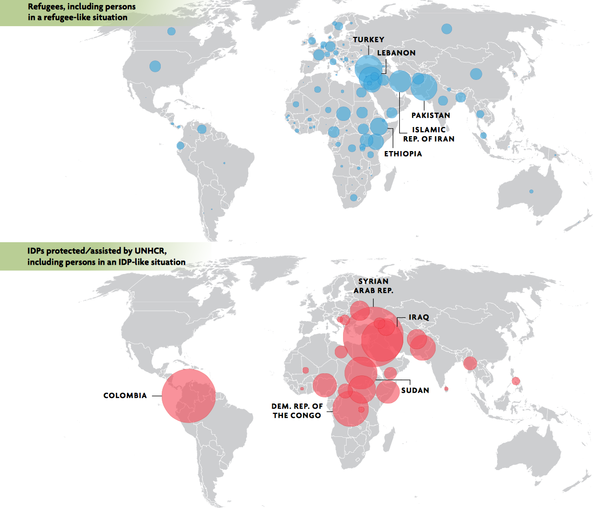
In this section, we focus on two applications that connect directly to the mission of the World Bank: financial inclusion and resilient financial systems.
The Problem of the Unbanked
It is estimated that about 35% of the world’s population did not have bank accounts of any kind as of 2017. Citizens of low income countries, the poor in general, and women in particular, are disproportionately affected.1 Refugees and the displaced can lose contact with their banks or have accounts locked or confiscated. In most countries, banks are not allowed to open accounts without doing KYC and AML checks, which automatically excludes the billion or more people who have no official identification.
Being unbanked leads to financial exclusion and makes it difficult for people to save money, get credit, start their own business, invest in education or health, manage risk, receive remittances or money transfers, keep their wealth safe, and in general, forces them into the shadow economy. Not surprisingly, the World Bank takes the position that “Financial inclusion is a key enabler to reducing poverty and boosting prosperity”.2
This unfortunate situation is not the fault of banks. Setting up a bank is costly. There are any number of regulatory and compliance measures that must be satisfied which requires lawyers, accountants, payment of fees, taxes, and sometimes bribes. Physical infrastructure is also required, including buildings, employees, and IT systems. On-boarding a new account holder at the least requires KYC and AML – this alone costs in the range of $40 per customer.
Of course, these costs must be passed onto the customer. Even in the US, accounts with low balances may pay monthly fees of $10 or more plus fees for each transaction. Holding $1,000 for a year in an account could easily cost $100 or more. The fixed cost of setting up accounts may simply not justify the benefits to either the bank or the customer when balances are too small.
As a result, the poorest and most vulnerable are left with a limited set of expensive and unattractive options. For example, the use of mobile phones to make money transfers is a growing business, especially in East Africa. However, costs are 1–2% on a $100 transaction and can range up to 10% on smaller transactions. Such services are not designed to make transfers over borders or in different currencies, and require the user to place his faith in the phone company as a TDI.
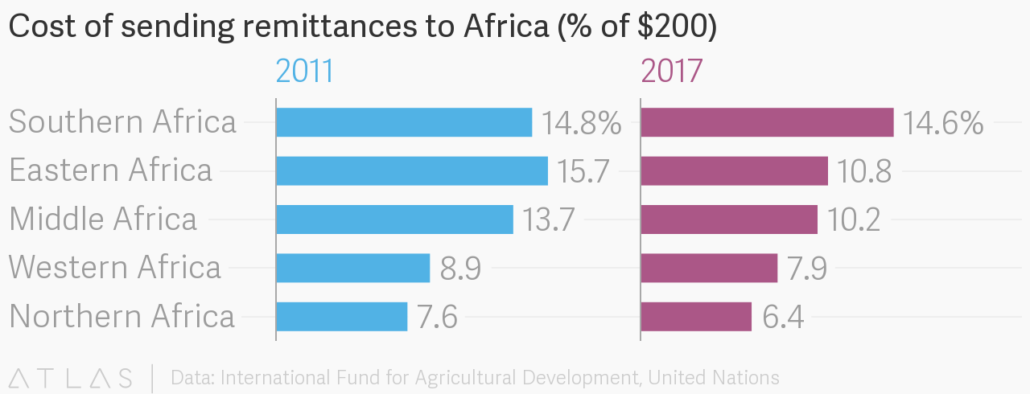
Receiving remittances from overseas can be quite expensive for the unbanked as well. Transaction fees ranged from 4–8% on average in 2018 and significant additional charges are added for foreign exchange services, using credit card and debit cards to fund transfers, and dispensing cash to the receiver. As a result, the unbanked often choose to transact only in cash. This makes them targets for criminals, especially as they attempt to build savings or a cash reserve.
Blockchain as a Solution
People who can afford it generally choose to have bank accounts because a bank’s traditional role is to keep money safe. Banks also facilitate payments between individuals, merchants and businesses, at a distance, and overseas. Cash carries security risks and, in an increasingly globalized and digital world, the uses of cash are becoming more limited.
The unbanked need an alternative to the formal banking sector and cash. Blockchain is a technology that has the potential to provide it. The most obvious advantage of blockchain and cryptocurrencies over banks and fiat accounts is cost. Although many existing implementations of blockchain have significant transactions fees, new approaches are fundamentally cheaper, for a number of reasons:
- Blockchains have no brick and mortar infrastructure.
- Blockchains are decentralized. They have no employees and do not have to pay auditors or lawyers to ensure regulatory compliance.
- It is easy to use blockchain without KYC/AML. Anyone can set up an account on the Bitcoin or Ethereum ledger, for example, and then any other user can transfer tokens into the account. By design, such transactions are anonymous.
- The fundamental cost of blockchain transactions are the value of the resources required by nodes to run the network.
Blockchains are ideally suited for small transactions and small accounts. Indeed, micropayments of less than a penny are some of the most important blockchain use cases since those enable all kinds of Machine to Machine (M2M) and Peer to Peer (P2P) markets that do not currently exist.
Blockchains are also very secure when correctly implemented and do not depend on TDIs. Therefore, they are well-suited for environments where local authorities may be corrupt or where institutions are weak.
On the blockchain, a person can retain anonymity. Women, religious or ethnic minorities, or other marginalized people can transact freely and anonymously without needing the permission or assistance of any authority.
Blockchain by its nature is transnational. Cryptocurrencies move freely across borders and can be accessed by displaced persons anywhere the internet is available.
Concerns and Limitations
Blockchain has the potential to greatly expand financial inclusion safely, cheaply, and securely, for the unbanked, the underbanked, and the poor who find paying for financial services tremendously burdensome. There are, however, a number of concerns that need to be addressed and limitations that must be acknowledged. Advances in blockchain and other technologies will make some issues relatively less important; for other issues, fundamental policy decisions must be made.
Blockchains are designed to allow anonymous transactions of cryptocurrencies. In particular, blockchains do not force account holders to undergo KYC/AML. As discussed above, this gives blockchain three key advantages over banks: low costs that make it feasible to maintain low balances or conduct small transactions, the ability to provide financial services to people without formal identification, and the ability to provide protection or anonymity to people and populations that otherwise might be at risk for exploitation or violence.
The most commonly cited concern is that forgoing KYC/AML to allow people to transact anonymously will provide new avenues for money laundering and tax evasion. Some claim these problems are deal breakers that should make cryptocurrencies completely unacceptable to any government or banking institution. We argue these concerns are overstated.
First, while it is structurally impossible to impose KYC/AML requirements on users within the blockchain environment itself, converting tokens into fiat currency and then moving them on or off chain usually requires making contact with the conventional banking system. Typically, a user would wire or make an ACH transfer into an account set up on a cryptocurrency exchange and then use the fiat balance to purchase tokens. To reverse the process, a user would sell tokens to someone else on the exchange for fiat and then have the proceeds wired back into his bank account. Thus, KYC/AML, tax reporting, and other regulatory requirements must be met when token value is moved off chain and into the real world.
Second, the gray economy is already enormous. Tax evasion, official corruption, weak institutions, embezzlement, financial crimes, cash transactions, barter, and a wide variety of money laundering techniques support a huge gray or underground economy worldwide. European countries as a group had gray economies that averaged 16.6% of official GDP in 2017. In 2015, 70 out of 159 countries worldwide had underground economies that were over 30% of official GDP, with Zimbabwe topping the list at 67% (Medina and Schneider, 2018). Clearly, KYC/AML and all of the other expensive efforts of the international banking system have had limited success in moving the underground economy into the open, and has been least successful where people are the poorest.
Financial crimes long preceded the advent of cryptocurrencies. To the extent that cryptocurrencies may provide a cheaper or more secure way to launder money or make illegal transactions, they probably are already being exploited as Bitcoin and Ethereum have been functioning for years. Furthermore, it is worth noting that the total market cap of all publicly traded cryptocurrencies was $250B as of this writing, while in 2018 Total World Product (GWP) was about $85T and total money supply including demand deposits worldwide were about $40T. In other words, cryptocurrency amounted to 0.6% of all money and only 0.3% of GWP.
Viewed against that backdrop, it is hard to believe that outlawing cryptocurrencies would have a significant impact on the underground economy. Similarly, it is hard to believe creating new cryptocurrencies would create very many new opportunities for underground activities beyond those already provided by existing ones. The fact remains that people who are paid by legally registered companies or who transact with legally registered merchants will still have their transactions reported and taxed. That is true regardless of whether credit cards, checks, cash, or cryptocurrency facilitate transactions. More importantly, to the extent that wider usage of cryptocurrencies leads to greater financial inclusion and economic prosperity, the result is likely to be a reduction in the size of the shadow economy.
John P. Conley, Professor of Economics at Vanderbilt University, Chief Economist at The Geeq Project. To learn more about our work at Geeq, please visit geeq.io
Acknowledgements:
Our thanks to Bill Maloney, Stephanie So, and the attendees of the World Bank Mini Boot Camp on Crypto, Information and ICT Economics for helpful discussions and comments.
Credits:
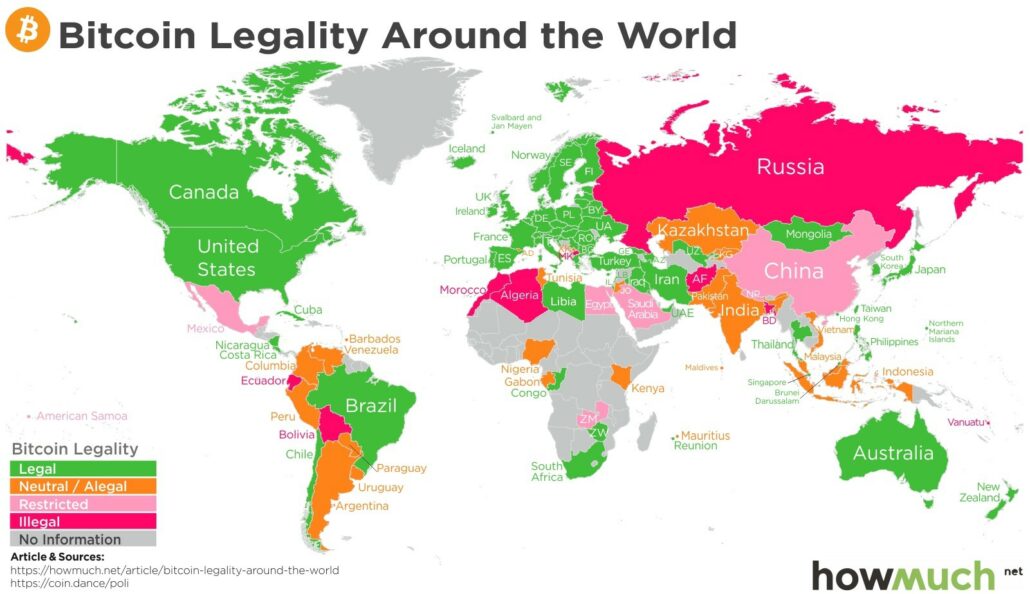
Figure 1 —https:// howmuch.net, a cost information website“Mapped: Bitcoin’s Legality Around The World” (January 5, 2018) https://howmuch.net/articles/bitcoin-legality-around-the-world
Figure 2 — UNHCR / I. Prickett, in Parater, L. “10 infographics that show the insane scale of global displacement” (June 20, 2015) https://www.unhcr.org/innovation/10-infographics-that-show-the-insane-scale-of-the-global-displacement-crisis/
Figure 3 —Data: International Fund for Agricultural Development, United Nations, Romero, L., Reporter, Quartz, https://www.theatlas.com/charts/HkF2xoB7b
close
Geeq™ at The World Bank
Thanks to all who attended or live-streamed the Blockchain and Crypto Boot Camp given by Chief Economist John Conley at The World Bank in Washington, DC last week. Hearing about the ongoing projects, conditions on the ground, and clients’ needs for real public blockchain solutions was valuable beyond measure.

Special thanks to William Maloney, Chief Economist of Equitable Growth, Finance, and Institutions (EFI) for organizing the workshop.
Photo by Plush Design Studio on Unsplash
close
Geeq Talks Micropayments at Scale
What do you get when you combine known technology (pre-images and hash digests) with:
Micropayments on decentralized blockchains.
How many?
All of them.
Tell your friends: this is the most fun they will ever have with algebra.
Please stay tuned! We’ll be back to share more soon.
close
Micropayments Take Center Stage in Geeq’s Testing Framework
Introducing Geeq Pay in Micropayments TF v0.2.1
Today, we released a milestone update to our testing framework by adding micropayment transactions.
By enabling micropayments at scale, Geeq’s on-chain transactions can provide an easy to use, consumer-oriented, decentralized payment platform enabling a new pay-as-you-go economy.
By making individual micropayments easier, more private, and less time-consuming than an online credit card transaction, you – and we – can break free from the restrictions of the old economy and help each other to help ourselves.
Don’t be the product, buy the product.
Geeq’s micropayments technology is able to turn the world right side up. This is the way Geeq’s open payments platform will work.
- Anyone who has an account in Geeq’s decentralized ecosystem will be able to pre-fund Geeq pennies to have on hand.
- As you browse independent websites and stores that are powered by Geeq Pay, but not controlled by Geeq in any way, you will be able to spend your pennies as you like, in only two or three clicks.
As a consumer, there is no need to accept cookies, keep track of the number of articles you’ve read lately, or login to a website with your email address.
As a creator, there is no need to worry about algorithms, advertisers, platforms that take big cuts, or arbitrary changes in rules that can upend your business overnight.
Geeq’s micropayments enable creators to be paid by anyone who appreciates them, charities to tap into small donations, and payment providers to drastically reduce their transaction costs. The days of limited options are numbered. The future is ours to make.
Here is a taste!
Try it Yourself!
To see the new framework in action and experiment with transactions on our demo site, click the link below and imagine the possibilities!
Yes, I’m in my Chrome browser and I’m ready to see Geeq’s MICROPAYMENTS TF v0.2.1 and GEEQ PAY!
What You Will Need
This testing framework is only supported in the Chrome desktop browser. You also need to install “Go Micro” from the Chrome Extension store.
The framework runs exclusively within your browser. To start over, refresh the browser. Once you close the window, it’s gone.
Let’s Build Web3 Together: Spread the Word About Geeq and Geeq Pay
The goal of the testing framework is to show the transformative potential of Geeq’s micropayments and inspire our community. So please spread the word to your friends and colleagues about Geeq and Geeq Pay and get in touch if you have a project and would like to collaborate.
Thank you for your support!
The Geeq Team
close
When is Blockchain Useful?
Geeq’s technology addresses an old problem: lack of trust due to asymmetric information. How can parties feel comfortable negotiating or transacting if one feels the other has an advantage in manipulating information?
Thus, Geeq is a new information and communications technology.
The primary economic value of services powered by Geeq is that they provide access to dependable, neutral, and correctly validated data sets.
In so doing, the data can be acceptable to all parties who wish to coordinate on some, but not all, dimensions with each other and do not wish to trust a third party.
How do we identify potential pain points?
There are five key criteria that make it likely that Geeq has a better approach to addressing a problem than conventional data systems or centralized cloud-based software as-a-service (SaaS) solutions:
- The problem requires secure transfer of value, possibly in very small increments; for example, micropayments for content or web services and machine to machine markets, and person to person payments such as small charitable contributions or sharing the cost of a meal among a group of friends.
- The problem involves agents who do not know or do not trust each other; for example, peer to peer markets for goods and services, escrows, and providing proof that all parties are what they say and behaved honestly.
- The problem involves many different actors from different organizations whose interests do not align; for example, logistics or chain of custody applications that transfer responsibilities from party to party.
- The problem requires objective provability of facts or data; for example, audit trails and telemetry collected from connected industrial, medical, and infrastructure devices.
- The problem involves agents who might wish to censor, alter, or hide data; for example, securities, land title, and financial transactions where theft and fraud are real possibilities.
For blockchain to offer a viable solution to these problems it must be secure, inexpensive and scalable. For Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) to become a realistic alternative to private databases, it needs to be flexible, upgradable, environmentally sustainable, and protect users from unreasonable volatility in token value.
close
Why is There No Mining at Geeq?
Bitcoin and Ethereum (among others) famously use mining in their Proof of Work (PoW) protocols, why doesn’t Geeq?
The short answer is: mining creates problematic incentives from the point of view of the user of a blockchain-based application.
Who Benefits from Mining? Miners.
Mining can be profitable for miners, who are in charge of the construction and maintenance of Proof of Work-based blockchains. That is why they do it.
An interesting feature of the mining market is that profits can be uncertain. The rewards change and sources of income are also fairly dynamic. In fact, the “block rewards” portion of their earnings are explicitly based on a mechanism that is a bit like playing a lottery. In a competitive market for mining, miners are incentivized to adopt strategies that give them an advantage.
We have already seen miners’ strategies adapt over time to maximize their profits. One response to the bitcoin blockchain, in particular, has been to set up mining “farms” comprised of many high powered computers. As the owner of many computers, a mining farm increases the odds it will make profits. This should not be surprising: it is like someone who buys many tickets to a lottery in order to increase their chances of winning.
For the user of PoW-based blockchains, these two features of the mining market introduce risks to the users that are out of their own control: a) miners have incentives that diverge from the users’ and b) mining sets up an uneven playing field. A more concentrated market for mining also concentrates power over the construction and maintenance of the Proof of Work-based blockchain. This means a PoW-based blockchain database is vulnerable to attack.
The most well-known vulnerability is the 51% attack, which has happened several times. There are other threats that are more complicated and also relatively unknown, so we will not include them here. Suffice to say that every potential threat introduces risk of disruptions in service and controversy, especially when attacks within protocol yield unexpected results. Some of the outcomes may result in transactions that are rolled back or censored, which is exactly what blockchain-based DApps are supposed to disallow.
Geeq is focused on providing value to the end user of any Geeq-enabled service.
As you use the Geeq platform, you have the security of knowing Geeq’s blockchain-based payment system is at the leading edge of blockchain technology. All Distributed Applications (DApps) built on the Geeq platform are based on underlying blockchain databases that have the integrity and dependability blockchains are supposed to have. As a result, DApp providers and consumers are able to focus on the quality of services DApps provide, with an emphasis on making them useful and easy to use.
Conclusion
Geeq’s Proof of HonestyTM (PoH) is a next generation, proprietary blockchain technology that enables a new hybrid platform. The platform itself is truly decentralized.
Geeq was built with the end goals of a blockchain-based, decentralized economy in mind. In order to arrive at that destination, we had to re-think all the layers of the blockchain “stack”, from the market for nodes and validators up through the final markets for new DApp-based goods and services.
Simply put, Geeq doesn’t have miners because their incentives are not aligned with our vision of a decentralized economy. In Geeq’s ecosystem, all incentives are aligned with those of the honest user, including the nodes and validators who construct and maintain the blockchains. At Geeq, market power doesn’t matter. Honesty does.
close





